Installation and Configuration of the Single-Tier "Express" Edition ODBC Driver for Sybase Data Sources, for Mac OS X
Review Preinstallation Documentation: Pre-Installation Requirements
Installation
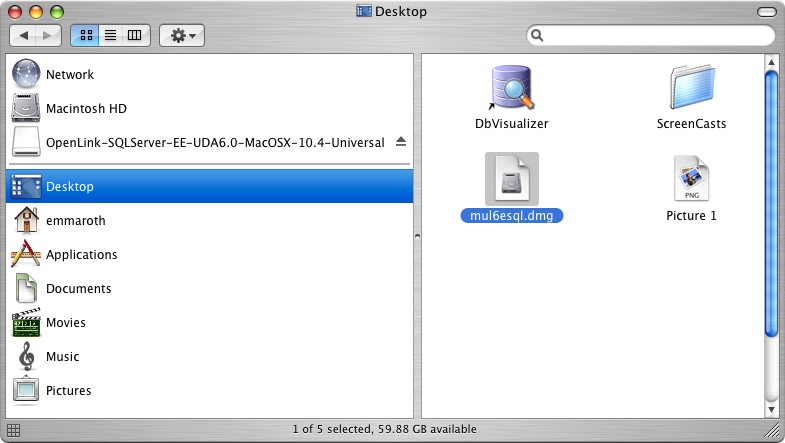
Note: The software must be installed as a user with Administrative privileges on the machine.- The Single-Tier "Express" Edition ODBC Driver for Sybase Data Sources is distributed as a Disk Image (.dmg) file:
- Double-click the disk image 'mul6esql.dmg' to access the installer .mpkg file:
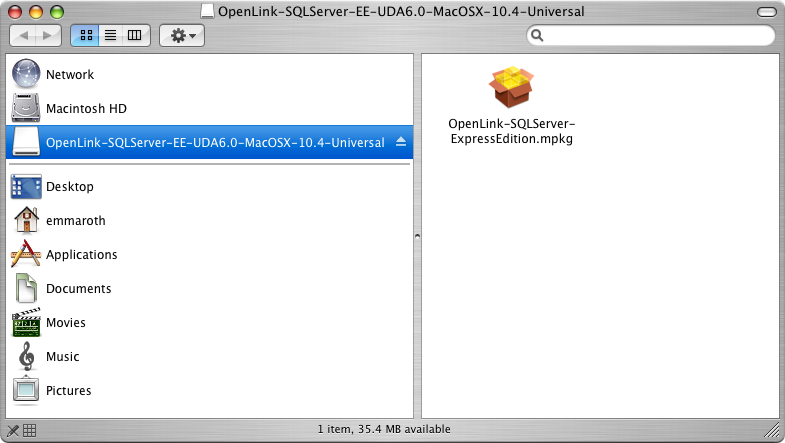
- Double-click the .mpkg file to run the installer and follow the instructions to complete the installation:
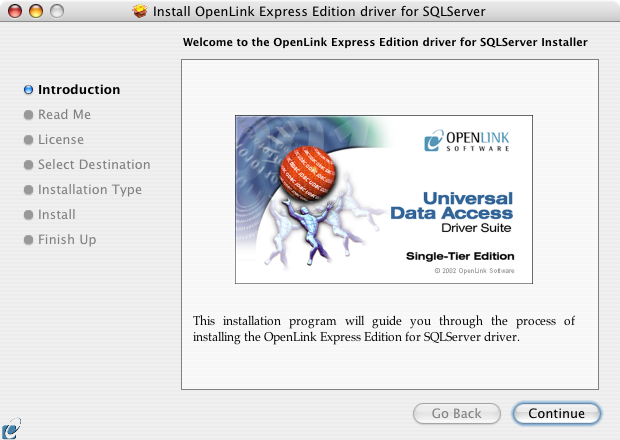
- This is the Welcome dialog for the
OpenLink ODBC Driver for SQL Server (Express Edition):
- Review the
Read Me file for installation requirements and known issues:
- Read the Software License Agreement:
- Agree to the Software License Agreement before continuing your installation:
- Select a destination volume for the driver installation:
- Choose to perform a custom or default installation of the driver:
- If you chose the custom option, select which of the following components to install:
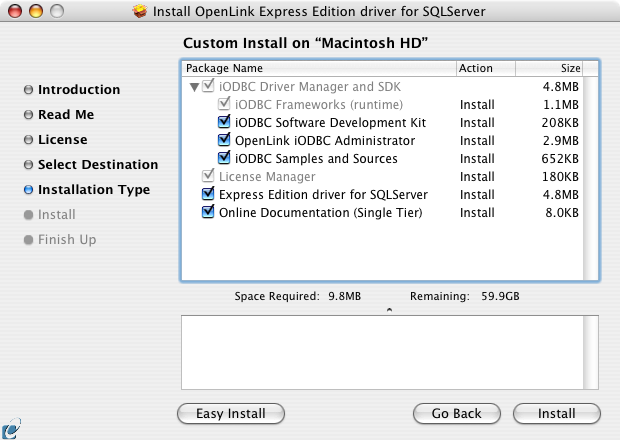
- Note: The Software must be installed as a user with Administrative privileges on the machine:
- After the driver has been installed, you will be prompted for a license file.
If a license file already exists on the machine, select the 'use existing file' option.
A trial (try) or full (buy) license can be obtained by selecting the 'try and buy' option which loads the online try and buy web page:
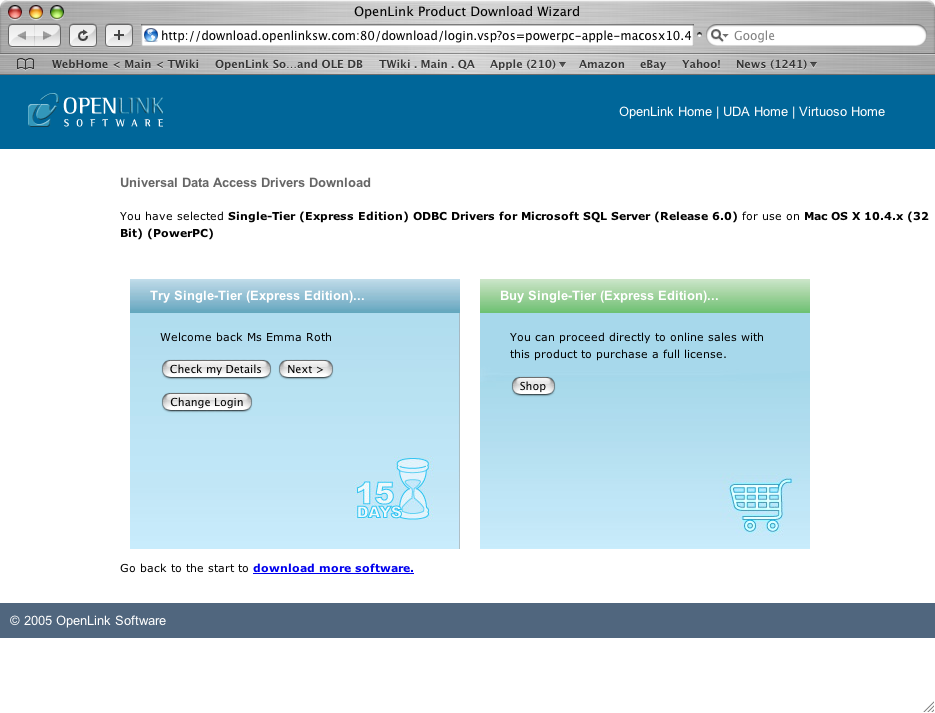
- To obtain the trial license you must be a registered user on the
OpenLink Web site and login with the username (e-mail address) and password for that user. Click on the 'Shop' link to visit the online shop cart to purchase a full license, if required:
- Click on the 'download license' button to obtain an immediate license file and save it to your desktop.
Alternatively, mail can be sent to your e-mail address with a link to your
OpenLink Data Space (ODS). Here, all trial and full license files will be stored in a specialized Briefcase for download at a later date.
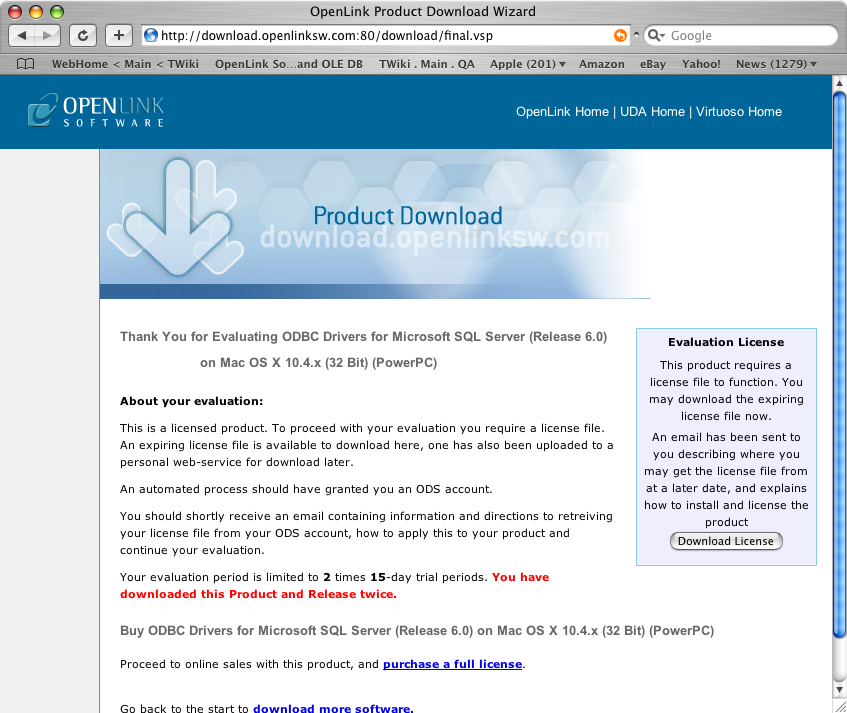
- Select the license file that you want to use for the installation:
- The installation is complete:
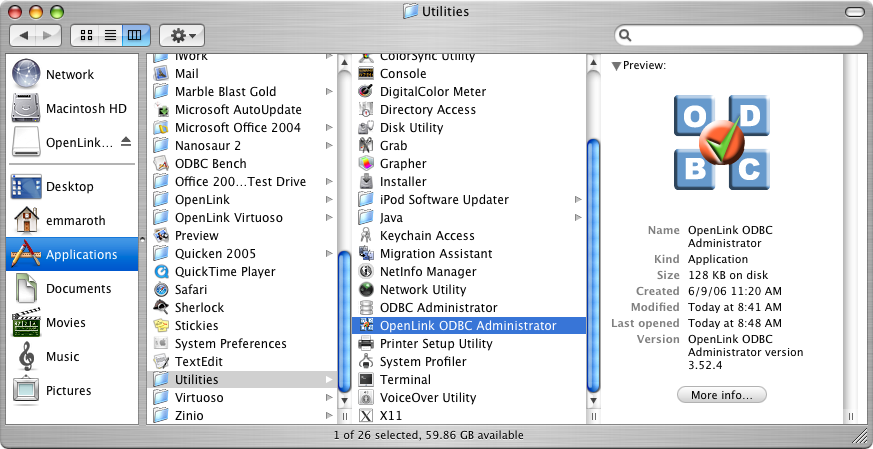
Configuration
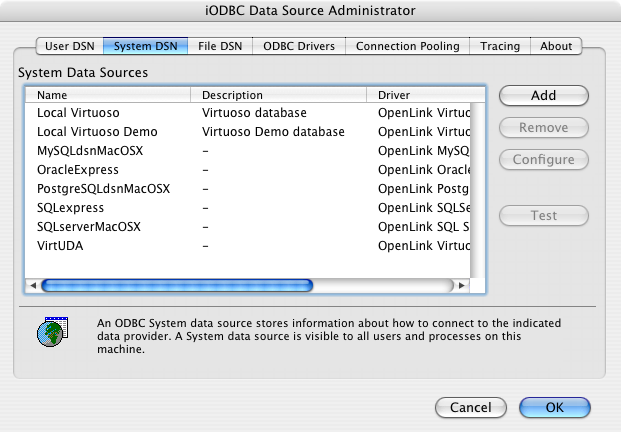
- To configure an ODBC DSN, run the
OpenLink iODBC Administrator located in the /Applications/iODBC folder:
- Click the Add button:
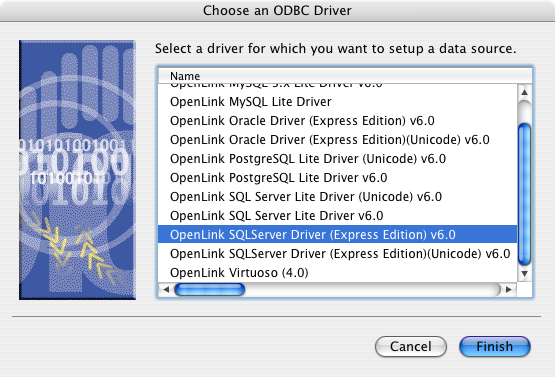
- Select the
OpenLink SQL Server Driver (Express Edition) v6.0 from the list of available drivers. Select the Unicode version of the driver if and only if you are working with multi-byte character sets, as unnecessary translations can significantly affect ODBC performance:
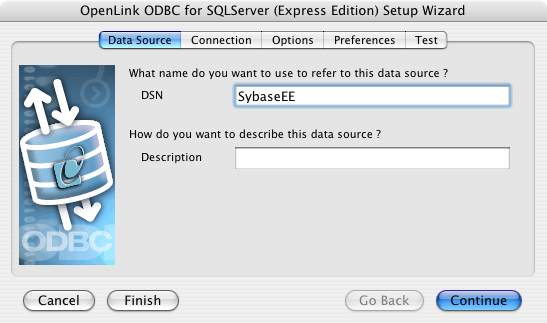
- Provide a suitable DSN name and optional description for the Data Source:
- The Connection Tab takes the minimum parameters required to make a connection to the target database:
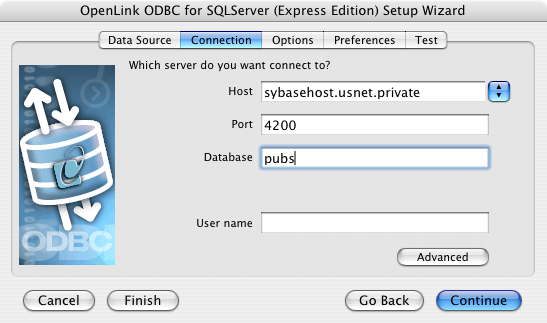
- Host - This is the fully qualified hostname or IP address of the machine hosting the DBMS you wish to access, e.g., dbms-server.example.com or 192.168.155.123.
Any hostname which can be resolved by your local DNS is acceptable.
- Port - This is the port on which SQL Server listens.
- Database - This is the SQL Server database to which you want to connect.
- User Name - This is a valid SQL Server user.
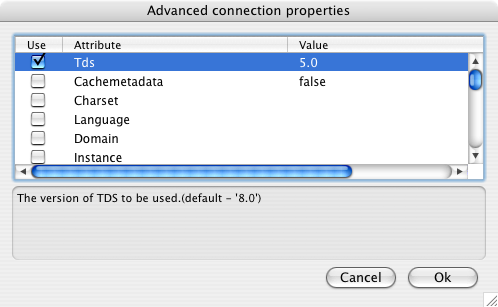
- The advanced button displays additional optional parameters that can be configured.
Attribute Name Description 
Wsid Workstation ID. No practical use. it's displayed by Enterprise Manager or Profiler associated with the connection. (default - the client host name) Cachemetadata When used with prepareSQL=3, causes the driver to cache column meta data for SELECT statements. Use with care. (default - false) NamedPipe When set to true, named pipe communication is used to connect to the database instead of TCP/IP sockets. When the os.name system property starts with 'windows' (case-insensitive), named pipes (both local and remote) are accessed through the Windows filesystem by opening a RandomAccessFile to the path. When the SQL Server and the client are on the same machine, a named pipe will usually have better performance than TCP/IP sockets since the network layer is eliminated. Charset Very important setting, determines the byte-value-to-character mapping for CHAR/VARCHAR/TEXT values. Applies for characters from the extended set (codes 128-255). Has no effect on NCHAR/NVARCHAR/NTEXT values since these are stored using Unicode. (default - the character set the server was installed with) PrepareSQL This parameter specifies the mechanism used for Prepared Statements. (default - 3 for SQL Server) SocketTimeout The time to wait (in seconds) for network activity before timing out. Use with care! If a non-zero value is supplied, this must be greater than the maximum time that the server will take to answer any query. Once the timeout value is exceeded, the network connection will be closed. This parameter may be useful for detecting dead network connections in a pooled environment.(default - 0) LoginTimeout The time to wait (in seconds) for a successful connection before timing out. If namedPipe is true and loginTimeout is non-zero, the value of loginTimeout is used for the retry timeout when 'All pipe instances are busy' error messages are received while attempting to connect to the server. If namedPipe is true and loginTimeout is zero (the default), a value of 20 seconds is used for the named pipe retry timeout. (default - 0) MaxStatements The number of statement prepares each connection should cache. A value of 0 will disable statement caching. (default - 500) PacketSize The network packet size (a multiple of 512). (default - 4096 when TDS is set to 7.0 or greater (Microsoft SQL Server 7.x and later); 512 when TDS is set to 4.2 or 5.0 (any Sybase version or Microsoft SQL Server 6.x and earlier) LobBuffer The amount of LOB data to buffer in memory before caching to disk. The value is in bytes for BLOB data and chars for CLOB data. (default - 32768) Tds The TDS version to be used. (default - '8.0') Domain Specifies the Windows domain in which to authenticate. If present, Windows (NTLM) authentication will be used instead of SQL Server authentication (i.e., the user and password provided are the domain user and password). This allows non-Windows clients to log in to servers which are only configured to accept Windows authentication. Ssl Specifies if and how to use SSL for secure communication. (default - off) MacAddress Network interface card MAC address. (default - '000000000000') Instance Named instance. SQL Server can run multiple 'named instances' (i.e., different server instances, running on different TCP ports) on the same machine. When using Microsoft tools, selecting one of these instances is made by using '[host_name]\[instance_name]' instead of the simple '[host_name]'. You must split the compound identifier, and use the instance name as a property. UseCursors Instructs the driver to use server side cursors instead of direct selects (also known as "firehose cursors") for forward-only, read-only result sets. (With other types of result sets, server- or client-side cursors are always used.) (default - false) LastUpdateCount If true, only the last update count will be returned by executeUpdate(). This is useful in case you are updating or inserting into tables that have triggers (such as replicated tables); there's no way to make the difference between an update count returned by a trigger and the actual update count, but the actual update count is always the last, as the triggers execute first. If false, all update counts are returned; use getMoreResults() to loop through them. (default - true) SendStringParametersAsUnicode Determines whether string parameters are sent to the SQL Server database in Unicode or in the default character encoding of the database. (default - true) UseLOBs Controls whether large types ( IMAGEandTEXT/NTEXT) should be mapped toLOBs by default when usinggetObject(). The default type constant returned is also controlled by this property:Types.BLOBforIMAGEandTypes.CLOBforTEXT/NTEXTwhentrue;Types.LONGVARBINARYforIMAGEandTypes.LONGVARCHARforTEXT/NTEXTwhenfalse. (default -true)BufferMinPackets Controls the minimum number of packets per statement to buffer to memory. Each Statement will buffer at least this many packets before being forced to use a temporary file if the [bufferMaxMemory] is reached, to ensure good performance even when one Statement caches a very large amount of data. (default - 8) BufferMaxMemory Controls the global buffer memory limit for all connections (in kilobytes). When the amount of buffered server response packets reaches this limit, additional packets are buffered to disk; there is however one exception: each Statement gets to buffer at least '[bufferMinPackets]' to memory before this limit is enforced. This means that this limit can and will usually be exceeded. (default - 1024) BatchSize Controls how many statements are sent to the server in a batch. The actual batch is broken up into pieces this large that are sent separately.(default - 0[unlimited] for SQL Server) ProgName Client library name. No practical use. It's displayed by Enterprise Manager or Profiler associated with the connection. AppName Application name. No practical use. It's displayed by Enterprise Manager or Profiler associated with the connection. Language ToBeDone TcpNoDelay true to enable TCP_NODELAY on the socket; false to disable it. (default - true)
- Host - This is the fully qualified hostname or IP address of the machine hosting the DBMS you wish to access, e.g., dbms-server.example.com or 192.168.155.123.
Any hostname which can be resolved by your local DNS is acceptable.
- Click continue to proceed to the Options tab.
This tab contains optional parameters that are not required for basic ODBC connectivity:
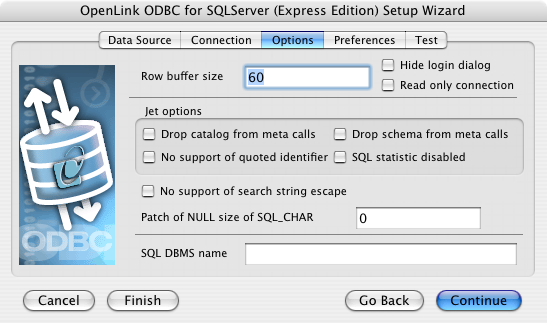
- Row Buffer Size - This attribute specifies the number of records to be transported over the network in a single network hop.
Values can range from 1 to 99.
- Hide Login Dialog - Suppresses the ODBC "Username" and "Password" login dialog boxes when interacting with your ODBC DSN from within an ODBC compliant application.
- Read Only connection - Specifies whether the connection is "Read-only." Make sure the check-box is unchecked to request a "Read/Write" connection.
- Drop Catalog from Meta calls - Enable this option to have the catalog name not appear for tables, views, and procedures when requesting database meta-data.
- No support of quoted identifier - If set, the call SQLGetInfo(SQL_IDENTIFIER_QUOTE_CHAR) will return a space (" ").
It can be used if the DBMS doesn't support quoted SQL like select * from "account."
- Drop Schema from Meta calls - Enable this option to have the schema-name not appear for tables, views, and procedures when requesting database meta-data.
- SQLStatistics disabled - Check this box to have SQLStatistics() return an empty result set.
Use this if the underlying database does not support retrieval of statistics about a table (e.g., what indexes it has).
- No support of search string escape - If set, the call SQLGetInfo(SQL_LIKE_ESCAPE_CLAUSE) will return a space (" ").
It can be used if the DBMS doesn't support SQL escape patterns.
- Patch of NULL size of SQL_CHAR - If set, this option overrides the size of SQL_CHAR column type returned by the database with the value set in the text box (in bytes).
With a default value of 0, the driver uses the size returned by the database.
- SQL_DBMS Name - Manually overrides the SQLGetInfo(SQL_DBMS_NAME) response returned by the driver.
This is required for products like Microsoft
InfoPath for which the return the value should be "SQL Server".
- Row Buffer Size - This attribute specifies the number of records to be transported over the network in a single network hop.
Values can range from 1 to 99.
- Click continue to proceed to the Preferences tab.
This tab contains optional parameters that are not required for basic ODBC connectivity:
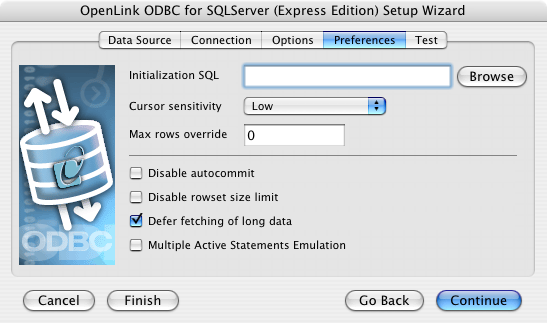
- Initialization SQL - Lets you specify a file containing SQL statements that will be run automatically against the database upon connection.
- Cursor Sensitivity - Enables or disables the row version cache used with dynamic cursors.
When dynamic cursor sensitivity is set high, the Cursor Library calculates checksums for each row in the current rowset and compares these with the checksums (if any) already stored in the row version cache for the same rows when fetched previously.
If the checksums differ for a row, the row has been updated since it was last fetched and the row status flag is set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED.
The row version cache is then updated with the latest checksums for the rowset.
From the user's point of view, the only visible difference between the two sensitivity settings is that a row status flag can never be set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED when the cursor sensitivity is low.
(The row status is instead displayed as SQL_ROW_SUCCESS.) In all other respects, performance aside, the two settings are the same.
Deleted rows don't appear in the rowset.
Updates to the row since the row was last fetched are reflected in the row data, and inserted rows appear in the rowset, if their keys fall within the span of the rowset.
If your application does not need to detect the row status SQL_ROW_UPDATED, you should leave the 'High Cursor Sensitivity' checkbox unchecked, as performance is improved.
The calculation and comparison of checksums for each row fetched carries an overhead.
If this option is enabled, the table oplrvc must have been created beforehand using the appropriate script for the target database.
- Max Rows Override - Allows you to define a limit on the maximum number of rows to be returned from a query.
The default value of 0 means no limit.
- Disable Autocommit - Changes the default commit behaviour of the
OpenLink driver. The default mode is AutoCommit (box unchecked).
- Disable Rowset Size Limit - Disables a limitation enforced by the cursor library.
This limitation is enforced by default.
It prevents the driver from claiming all available memory in the event that a resultset generated from an erroneous query is very large.
The limit is normally never reached.
- Defer fetching of long data - Defers fetching of LONG (BINARY, BLOB etc.) data unless explicitly requested in a query.
This provides significant performance increases when fields in query do not include LONG data fields.
- Multiple Active Statements Emulation - Enables use of Multiple Active statements in an ODBC application even if the underlying database does not allow this, as it is emulated in the driver.
- Initialization SQL - Lets you specify a file containing SQL statements that will be run automatically against the database upon connection.
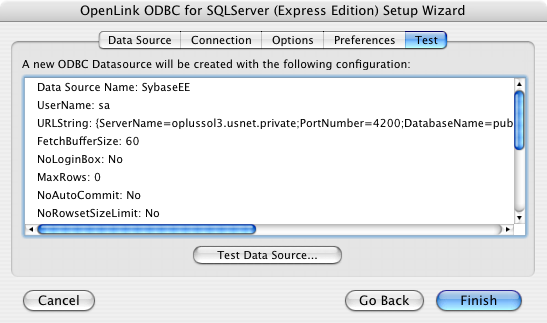
- Click on the 'Test Data Source' button to make a connection to the database to verify connectivity:
Next...
- Test your DSNs with our sample program.
- If anything isn't working as you expect, including errors resulting from the test above, see our Troubleshooting Resources.
- Should you decide to purchase a commercial license at the end of your evaluation period, be sure to consult our documentation which explains the placement and uptake of commercial license files and the use of our
OpenLink License Manager technology: License Technology & Application.
