Installation and Configuration of the Single-Tier "Express" Edition ODBC Driver for
Review Preinstallation Documentation: Pre-Installation Requirements
Installation
Note: The software must be installed as a user with Administrative privileges on the machine.- The Single-Tier "Express" Edition ODBC Driver for
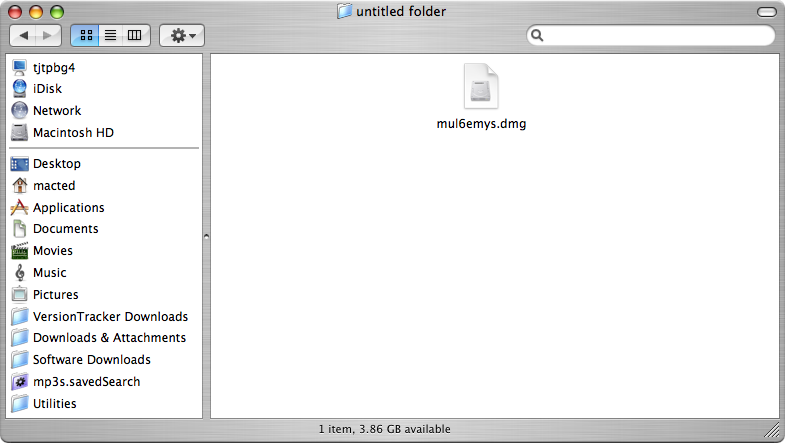
MySQL Data Sources is distributed as a Disk Image (.dmg) file: 
- Double-click the disk image 'mul6emys.dmg' to access the installer .mpkg file:
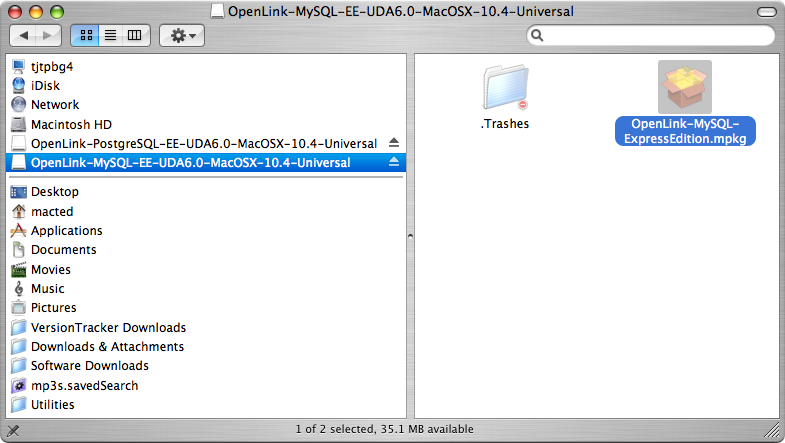
- Double-click the .mpkg file to run the installer and follow the instructions to complete the installation:
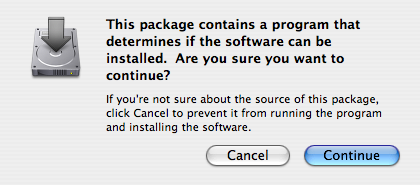
- When prompted, permit the verification script to run.
The script checks to see that you are running a version of Mac OS X later than 10.3.0:
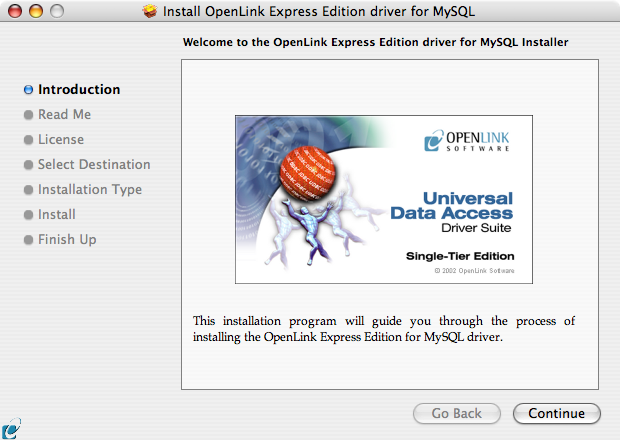
- Review the Welcome message to confirm you're installing the right driver:
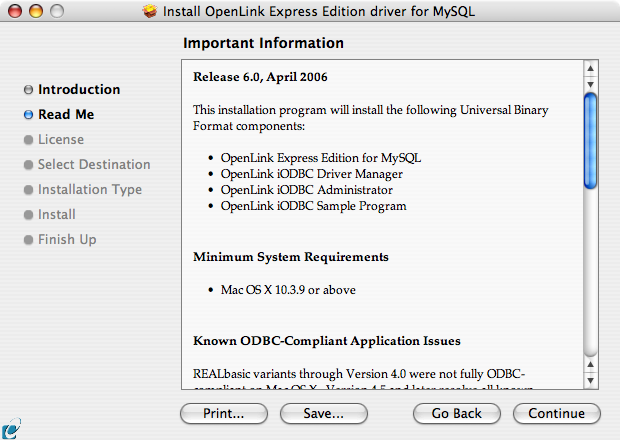
- Review the Read Me for installation requirements and any known issues:
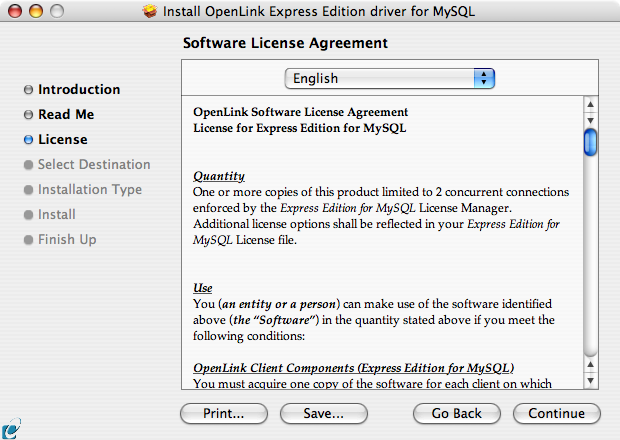
- Read the Software License Agreement:
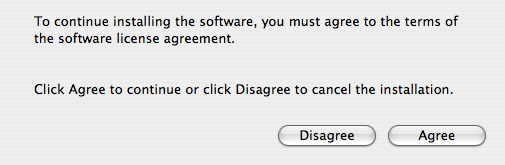
- Agree to the Software License Agreement before continuing your installation:
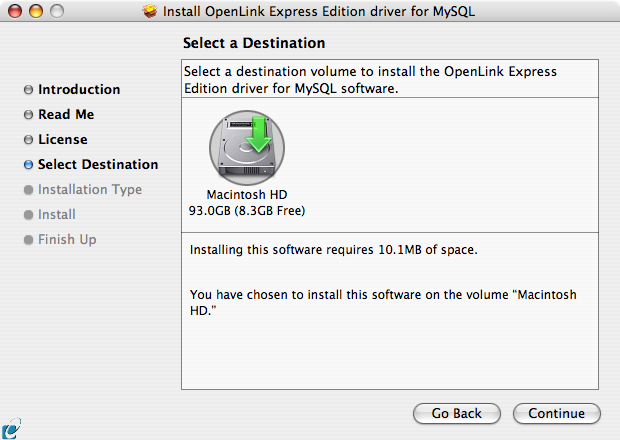
- Select the destination volume for the driver installation:
- Accept the default installation of the driver or click Customize to select specific components for installation:
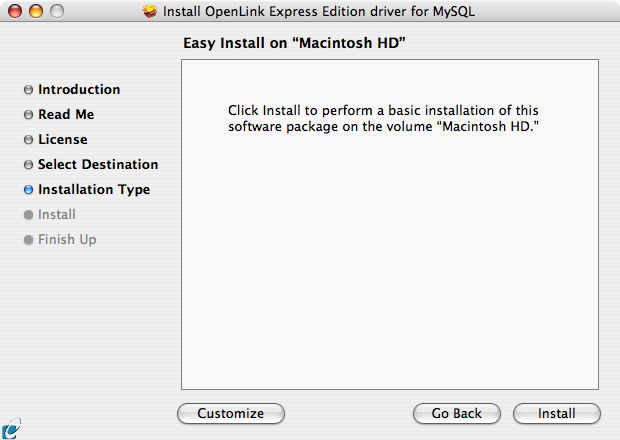
- Select the components to be installed or click Easy Install to return to the default:
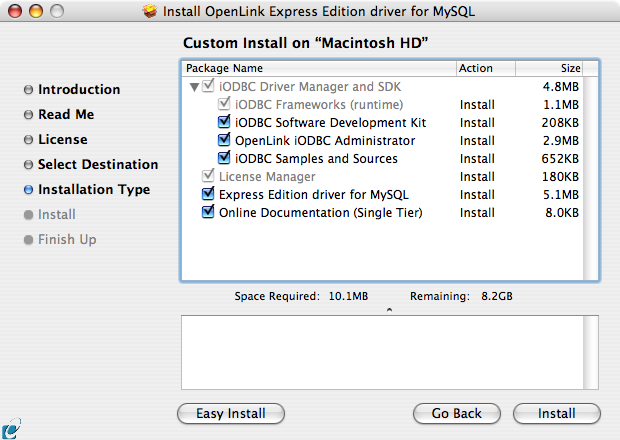
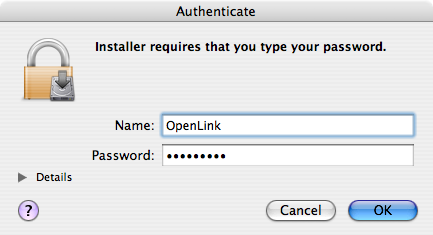
- The software must be installed as a user with Administrative privileges on the machine.
When prompted, provide a relevant username and password:
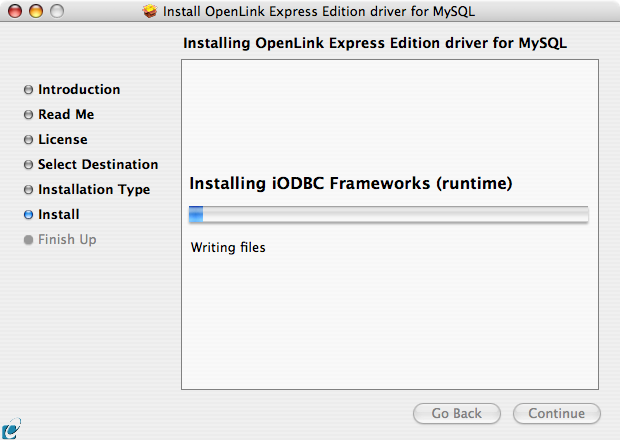
- Installation will proceed.
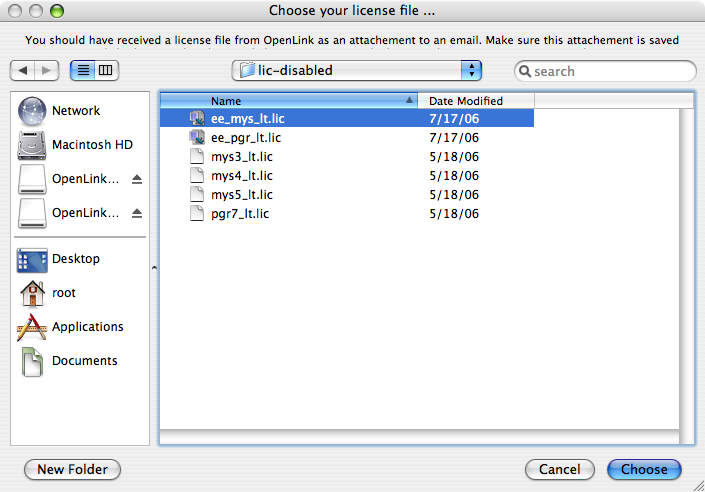
- During installation, you will be prompted to select a license file for the driver.
If such a license file already exists on the machine, then select the 'use existing file' option.
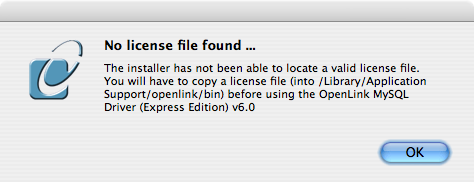
- If you accidentally clicked this option, you can cancel out of the selection dialog.
As the following alert will explain, you can manually apply the license file at any point in the future:
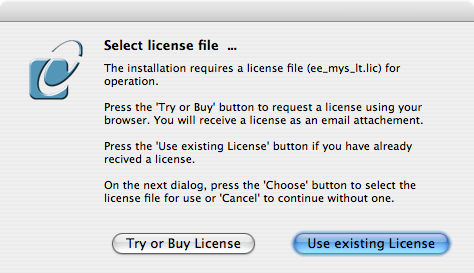
- A trial or permanent license may be obtained by selecting the Try and Buy option which loads our online try and buy web page:
- A permanent license may be obtained by clicking on the 'Shop' link to visit our online store, or you may obtain a trial license by registering with and logging in to the
OpenLink Web site: 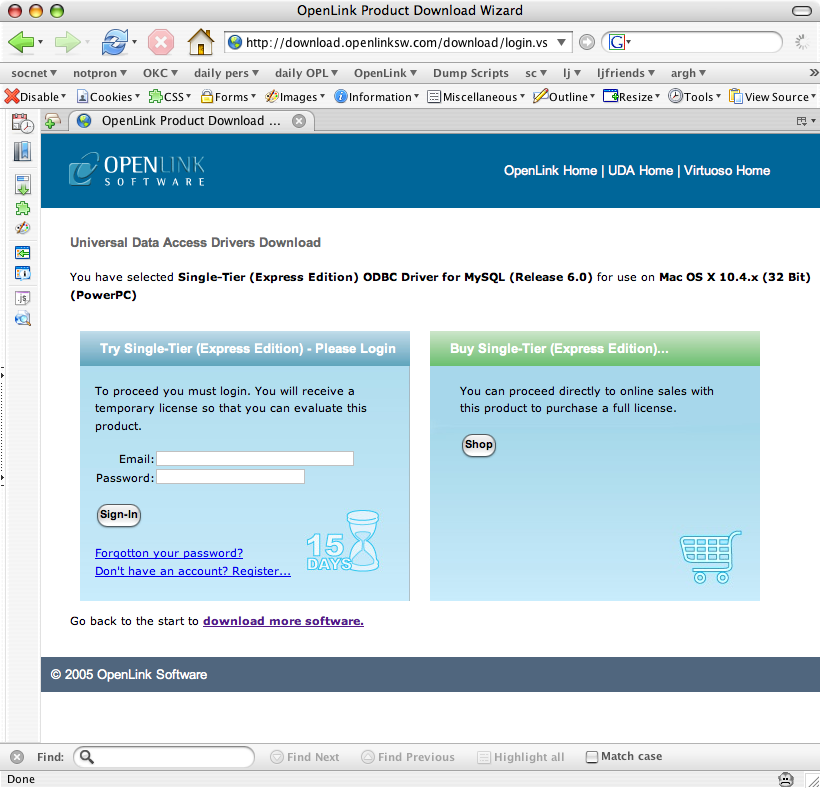
- Click on the 'Download License' button to immediately obtain an evaluation license file.
It will be saved to your browser's download folder (which typically defaults to your desktop).
A message will also be sent to your email address with a link to your
OpenLink Data Space (ODS) Briefcase, where all non-expired trial and full license files will be stored for download at your convenience. 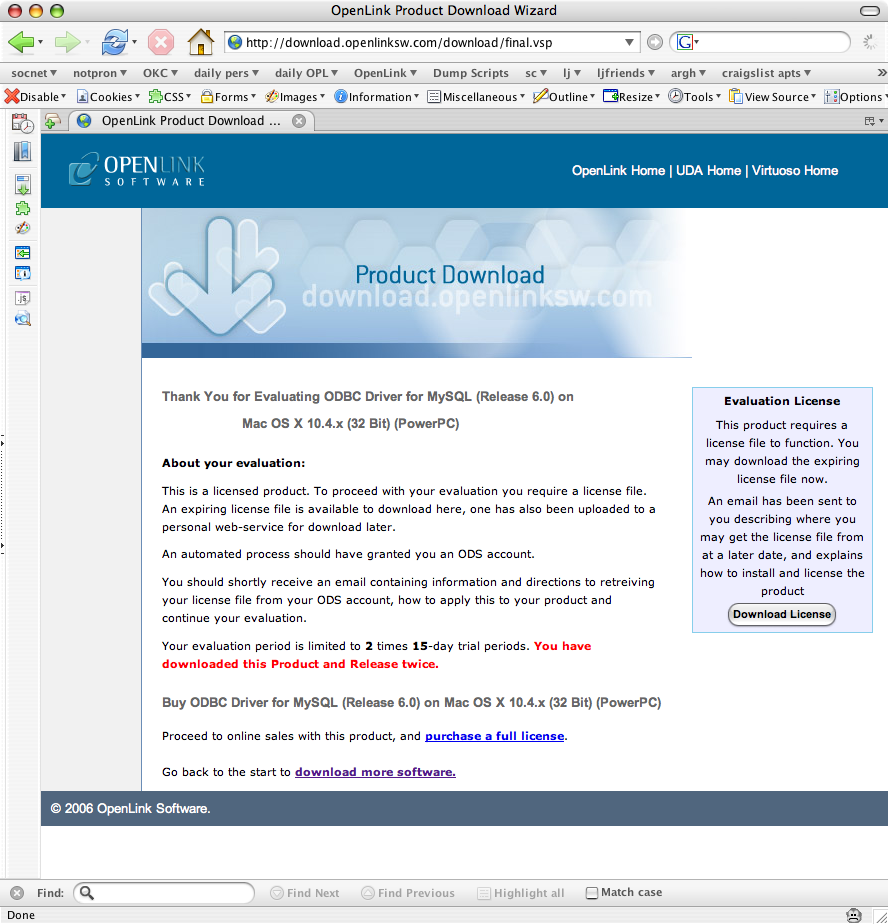
- Close the browser and proceed as if you had selected the option to use existing file.
Select the license file to be used for the installation:

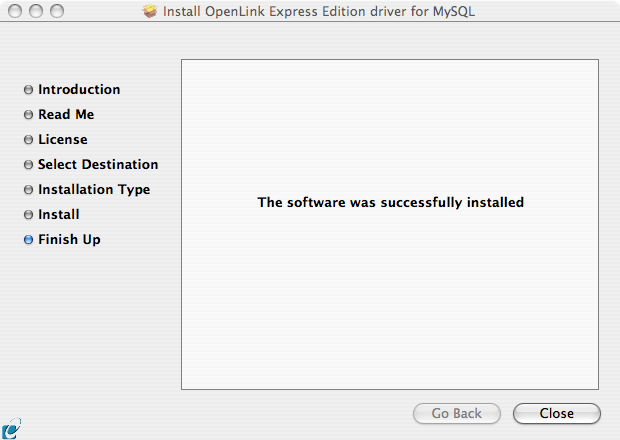
- Installation is now complete, and you can exit the installer and proceed to configure a DSN:
Configuration
- To configure an ODBC DSN, run the
OpenLink iODBC Administrator located in the /Applications/iODBC folder: 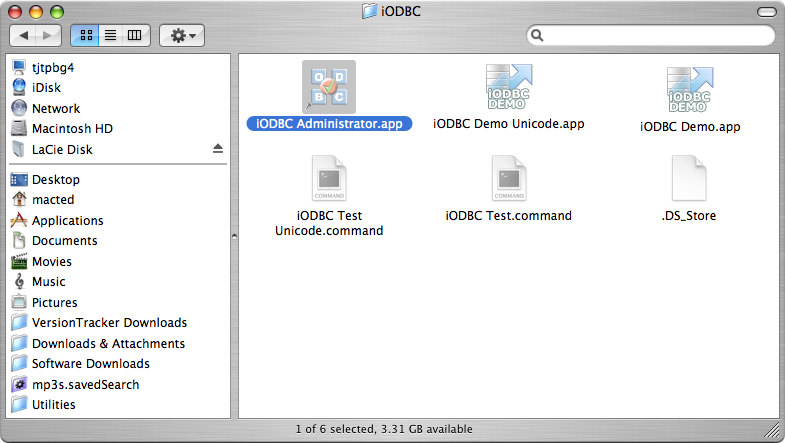
- Click the Add button:
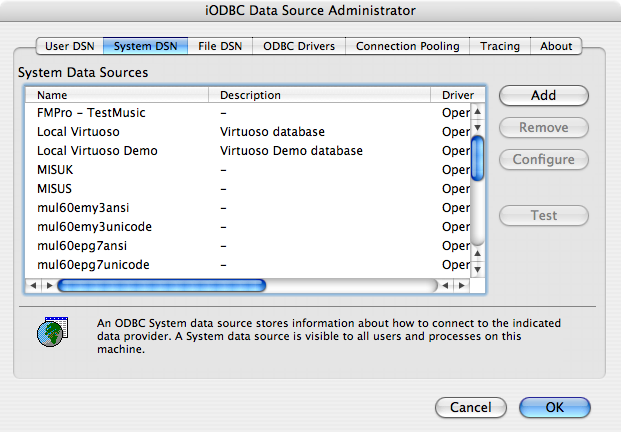
- Select the
OpenLink MySQL Driver (Express Edition)(Unicode) v6.0 if and only if you are working with multi-byte character sets, as unnecessary translations can significantly ODBC performance: 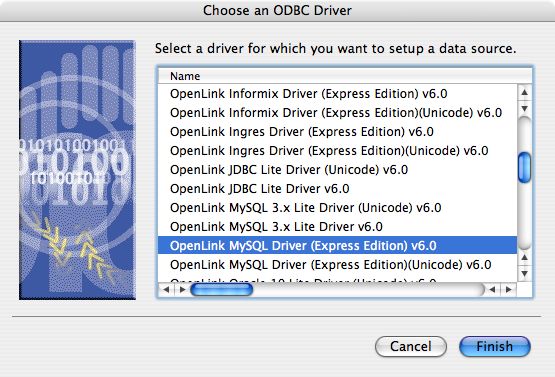
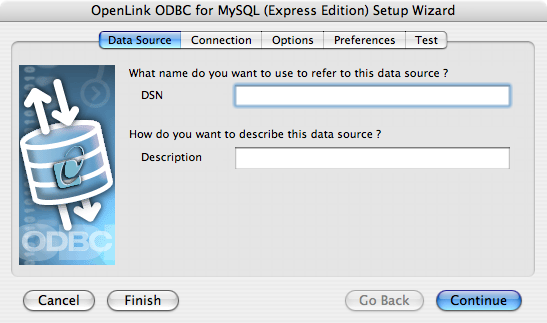
- Provide a suitable DSN name and optional description for the Data Source:
- The Connection Tab takes the minimum parameters required to make a connection to the target database:
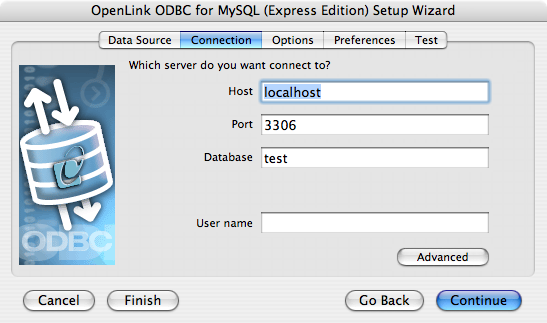
- Host - the hostname of the server on which the target
MySQL instance is running - Port - the port at which the target
MySQL instance is listening (default 3306) - Database - the database name of a valid database on the target
MySQL instance - User name - a valid
MySQL username - The advanced button displays additional, optional parameters that can be configured.
Name Description SocketFactoryClassName The name of the class that the driver should use for creating socket connections to the server. This class must implement the interface 'com. MySQL.jdbc.SocketFactory' and have a public no-args constructor. ConnectTimeout Timeout for socket connect (in milliseconds), with 0 being no timeout. SocketTimeout Timeout on network socket operations (0, the default means no timeout). IsInteractiveClient Set the CLIENT_INTERACTIVE flag, which tells MySQL to timeout connections based on INTERACTIVE_TIMEOUT instead of WAIT_TIMEOUT UseCompression Use zlib compression when communicating with the server (true/false). AllowMultiQueries Allow the use of ';' to delimit multiple queries during one statement (true/false). UseSSL Use SSL when communicating with the server (true/false), defaults to 'false'. RequireSSL Require SSL connection if useSSL is true? AllowUrlInLocalInfile Should the driver allow URLs in 'LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE' statements? Paranoid Take measures to prevent exposure sensitive information in error messages and clear data structures holding sensitive data when possible? MetadataCacheSize The number of queries for which to cacheResultSetMetadata, if cacheResultSetMetaData is set to 'true' BlobSendChunkSize Chunk to use when sending BLOB/CLOBs via ServerPreparedStatements CacheServerConfiguration Should the driver cache the results of 'SHOW VARIABLES' and 'SHOW COLLATION' on a per-URL basis? ElideSetAutoCommits If using MySQL-4.1 or newer, should the driver only issue set autocommit = n queries when the server's state doesn't match the requested state by Connection.setAutoCommit(boolean)? UseReadAheadInput Use newer, optimized non-blocking, buffered input stream when reading from the server? UseUnicode Should the driver use Unicode character encodings when handling strings? Should only be used when the driver can't determine the character set mapping, or you are trying to 'force' the driver to use a character set that MySQL doesn't natively support (such as UTF-8), true/false. CharacterEncoding If 'useUnicode' is set to true, what character encoding should the driver use when dealing with strings? (defaults is to 'autodetect') CharacterSetResults Character set used by the server to return result sets ConnectionCollation If set, tells the server to use this collation via 'set collation_connection'. SessionVariables A comma-separated list of name/value pairs to be sent as SET SESSION ... to the server when the driver connects.
- Host - the hostname of the server on which the target
- Click continue to proceed to the Options tab.
This tab contains optional parameters that are not required for basic ODBC connectivity:
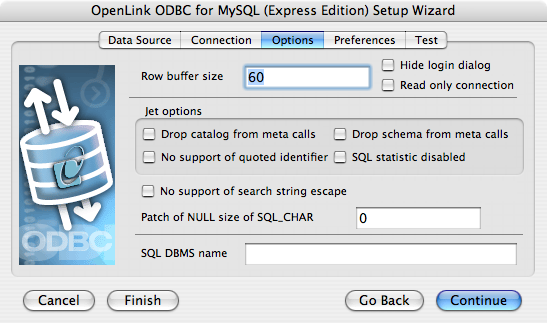
- Row Buffer Size - This attribute specifies the number of records to be transported over the network in a single network hop.
Values can range from 1 to 99.
- Hide Login Dialog - Suppresses the ODBC "Username" and "Password" login dialog boxes when interacting with your ODBC DSN from within an ODBC compliant application.
- Read Only connection - Specifies whether the connection is "Read-only." Make sure the checkbox is unchecked to request a "Read/Write" connection.
- Drop Catalog from Meta calls - Enable this option to have the catalog name not appear for tables, views, and procedures when requesting database meta-data.
- No support of quoted identifier - If set, the call
SQLGetInfo for 'SQL_IDENTIFIER_QUOTE_CHAR' will return a space (" "). It can be used if the DBMS doesn't support quoted SQL like select * from "account." - Drop Schema from Meta calls - Enable this option to have the schema-name not appear for tables, views, and procedures when requesting database meta-data.
- SQLStatistics disabled - Check this box to have SQLStatistics() return an empty resultset.
Use this if the underlying database does not support retrieval of statistics about a table (e.g.
what indexes it has).
- No support of search string escape - If set, the call
SQLGetInfo for 'SQL_LIKE_ESCAPE_CLAUSE' will return a space (" "). It can be used if the DBMS doesn't support SQL escape patterns. - Patch of NULL size of SQL_CHAR - If set, this option overrides the size of SQL_CHAR column type returned by the database with the value set in the text box (in bytes).
With a default value of 0, the driver uses the size returned by the database.
- SQL_DBMS Name - Manually overrides the
SQLGetInfo(SQL_DBMS_NAME) response returned by the driver. This is required for products like Microsoft vInfoPath for which the return the value should be "SQL Server".
- Row Buffer Size - This attribute specifies the number of records to be transported over the network in a single network hop.
Values can range from 1 to 99.
- Click continue to proceed to the Preferences tab.
This tab contains optional parameters that are not required for basic ODBC connectivity:
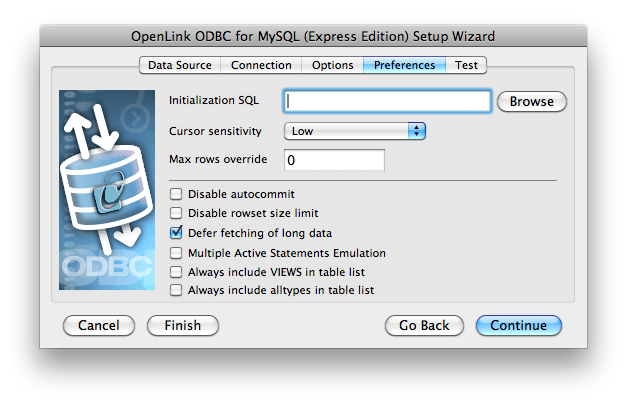
- Initialization SQL - Lets you specify a file containing SQL statements that will be run automatically against the database upon connection.
- Cursor Sensitivity - Enables or disables the row version cache used with dynamic cursors.
When dynamic cursor sensitivity is set high, the Cursor Library calculates checksums for each row in the current rowset and compares these with the checksums (if any) already stored in the row version cache for the same rows when fetched previously.
If the checksums differ for a row, the row has been updated since it was last fetched and the row status flag is set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED.
The row version cache is then updated with the latest checksums for the rowset.
From the user's point of view, the only visible difference between the two sensitivity settings is that a row status flag can never be set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED when the cursor sensitivity is low.
(The row status is instead displayed as SQL_ROW_SUCCESS.) In all other respects, performance aside, the two settings are the same.
Deleted rows don't appear in the rowset.
Updates to the row since the row was last fetched are reflected in the row data, and inserted rows appear in the rowset, if their keys fall within the span of the rowset.
If your application does not need to detect the row status SQL_ROW_UPDATED, you should leave the 'High Cursor Sensitivity' checkbox unchecked, as performance is improved.
The calculation and comparison of checksums for each row fetched carries an overhead.
If this option is enabled, the table oplrvc must have been created beforehand using the appropriate script for the target database.
- Max Rows Override - Allows you to define a limit on the maximum number of rows to be returned from a query.
The default value of 0 means no limit.
- Disable Autocommit - Changes the default commit behaviour of the
OpenLink driver. The default mode is AutoCommit (box unchecked). - Disable Rowset Size Limit - Disables a limitation enforced by the cursor library.
This limitation is enforced by default.
It prevents the driver from claiming all available memory in the event that a resultset generated from an erroneous query is very large.
The limit is normally never reached.
- Defer fetching of long data - Defers fetching of LONG (BINARY, BLOB etc.) data unless explicitly requested in a query.
This provides significant performance increases when fields in query do not include LONG data fields.
- Multiple Active Statements Emulation - Enables use of Multiple Active statements in an ODBC application even if the underlying database does not allow this, as it is emulated in the driver.
- Initialization SQL - Lets you specify a file containing SQL statements that will be run automatically against the database upon connection.
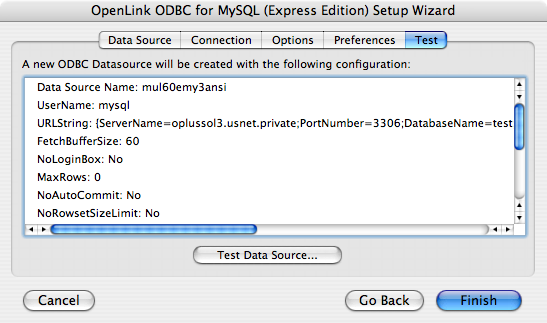
- Click on the 'Test Data Source' button to make a connection to the database to verify connectivity:
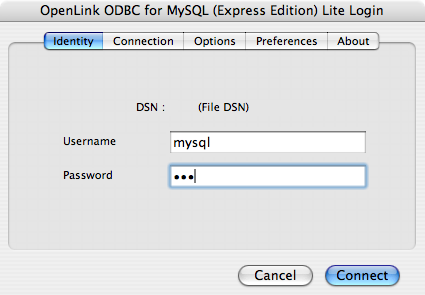
- Enter a valid username and password for the database:
- A successful connection to the database has been made:
Next...
- Test your DSNs with our sample program.
- If anything isn't working as you expect, including errors resulting from the test above, see our Troubleshooting Resources.
- Should you decide to purchase a commercial license at the end of your evaluation period, be sure to consult our documentation which explains the placement and uptake of commercial license files and the use of our
OpenLink License Manager technology: License Technology & Application.