Single-Tier Licensing Models
Our Single-Tier licenses are based on a Client/Server or Application Server model. This page describes the licensing models and shows the various architectures to which the license models apply.
Workstation
Our Workstation license is appropriate for architectures wherein one or more workstation machines host a number of SQL compliant applications.
These SQL applications open up a number of DB sessions through which a number of queries are piped to a DBMS
Workstations machines tend to be Mac or Windows desktops. They never support more than one user at one time. Applications tend to be spreadsheets, report building tools, or other end-user applications. Licenses are deployed on each client machine, as each client machine constitues a user. These licenses usually have a moderate pool of concurrent users and connections to meet the immediate needs of end users who utilize the software.
IMPORTANT: We requires that machines running Server-class operating systems (e.g., Windows Server, Mac OS X Server, Solaris, AIX, HP-UX) be licensed under the Application Server model. This is true even when the machine would otherwise be classed as a Workstation.Basic Workstation
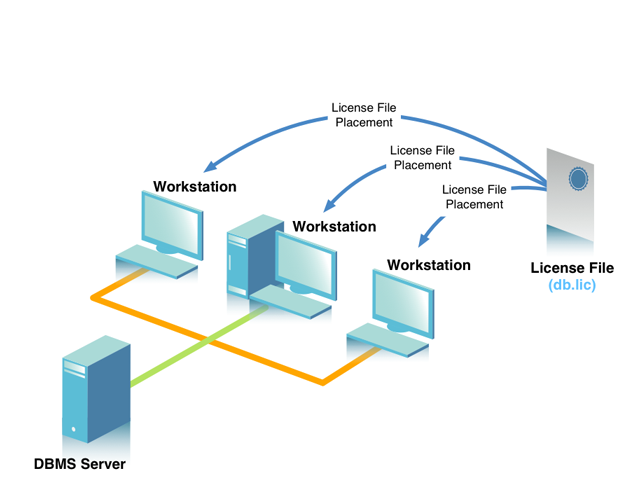
One or more workstations contain a SQL client application and our Single-Tier driver. The workstation or workstations may or may not contain a database native client, depending on the target DBMS and capabilities of the Single-Tier driver. The DBMS resides on a remote server.
Application Server
Our Application Server license is appropriate for architectures wherein multiple, remote clients connect to a centralized server that hosts Application Server software that manages and serves clients by returning SQL data from a DBMS via our Single-Tier drivers. The server software and Single-Tier drivers must reside on the same machine. The Application Server may or may not contain a database native client, depending on the target DBMS and capabilities of the Single-Tier driver. This Application Server software may reside on a dedicated server, or it may reside on the DBMS server.
Application Server architectures tend to comprise Application Server software deployed on powerful, multi-processor core, Unix or Linux machines. They are capable of supporting multi-le users simultaneously. Thread-safety, parallel execution, load balancing, fail-safety, and other features associated with one or more SQL compliant application instances for resilient, high volume, mission critical computing are the key characteristics of this model. The Application Server license(s) can be deployed on a single server or server cluster and usually contains a large or unlimited pool of connections to meet the needs of its many clients.
IMPORTANT: We requires that machines running Server-class operating systems (e.g., Windows Server, Mac OS X Server, Solaris, AIX, HP-UX) be licensed under the Application Server model. This is true even when the machine would otherwise be classed as a Workstation. Dedicated Application Server
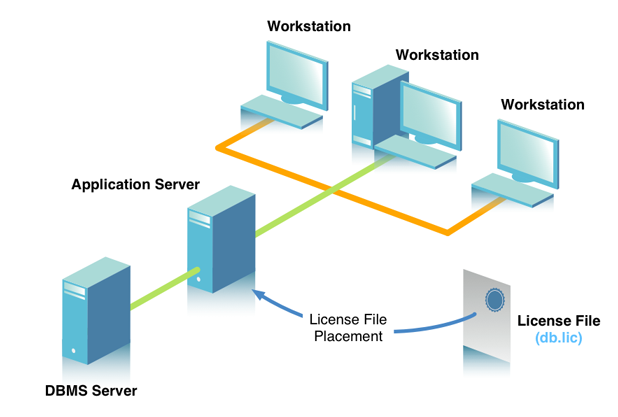
Remote clients or dumb terminals connect to a dedicated Application Server that contains a SQL compliant client application and our Single-Tier drivers. The Application Server may or may not contain a database native client, depending on the target DBMS and capabilities of the Single-Tier driver.The DBMS resides on a distinct server.
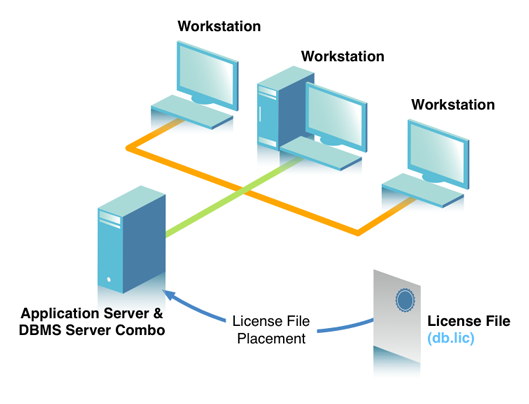
Dual-Purpose Application & DBMS Server
Remote clients or dumb terminals connect to a dedicated application server that contains a SQL compliant client application, our Single-Tier drivers, and the DBMS.