ADO .NET Data Access Providers - Logical Diagrams
This section provides logical diagrams for OpenLink's ADO .NET data access providers. Single-Tier (Lite Edition) Drivers Multi-Tier Drivers Single-Tier (Lite Edition) Drivers
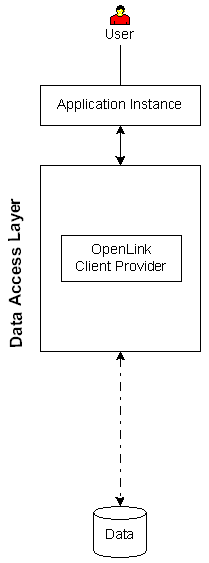 | Executive Summary: A clientside-only solution that provides enterprise grade data access with minimal configuration.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), OpenLink Client Provider, Data Repository.
Functional Capabilities: .NET-based data access to Microsoft SQL Server and Sybase data stores.
Hardware/OS Dependencies: OpenLink Client Provider must be installed on a supported operating system that contains a functional .NET framework.
The .NET framework version may vary depending on the OpenLink provider version.
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
Other Dependencies:
Performance Levels: Highest performance available.
Implementation Variances: 1) All Architectural Components may reside on the same machine, 2) Data store may reside on a remote machine.
Security Features:
Constraints & Limitations:
|
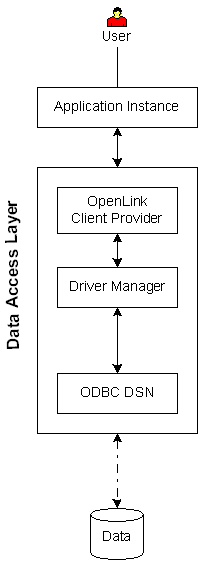 | Executive Summary: A clientside-only solution that provides enterprise grade data access with minimal configuration.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), OpenLink Client Provider, ODBC Driver Manager, ODBC DSN, Data Repository.
Functional Capabilities: .NET data access to SQL data stores via ODBC data sources.
Hardware/OS Dependencies: OpenLink Client Provider must be installed on a supported operating system that contains a functional .NET framework.
The .NET framework version may vary depending on the OpenLink provider version.
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
Other Dependencies: OpenLink Client Provider must be installed on a system that contains a functional ODBC DSN that connects to the target data repository.
The ODBC DSN may use OpenLink or non-OpenLink drivers.
The ODBC Drivers on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor as the OpenLink Client Provider, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
Performance Levels: High.
Implementation Variances: 1) All Achitectural Components may reside on the same machine, 2) Data Store may reside on a remote machine.
Security Features:
Constraints & Limitations: Solution applies only to data stores that are accessible via ODBC DSNs.
|
Multi-Tier Drivers
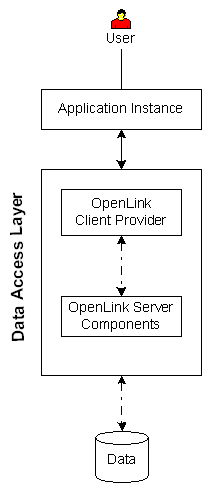 | Executive Summary: A client/server solution that provides enterprise grade data access with maximum configuration, security, and diagnostic resources.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, OpenLink Server Components, Data Repository.
Functional Capabilities: .NET data access to supported data stores.
Hardware/OS Dependencies: OpenLink Client Driver must be installed on a supported operating system that contains a functional JRE.
The JRE version may vary depending on the OpenLink client driver version..
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
OpenLink Server Components must be installed on a supported operating system.
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
Other Dependencies: OpenLink Server Components must reside on same machine as data store when that data store is a DB2, Informix, Ingres, Oracle, or Progress DBMS.
This restriction does not apply when the target data store is a Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Sybase DBMS.
Performance Levels: High performance.
Implementation Variances: 1) All Architectural Components may reside on one machine, 2) OpenLink server components and data store may reside on one, distinct server, 3) OpenLink server components may reside on a gateway and data store may reside on a dedicated DBMS server.
This architecture is suitable only for connectivity to Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Sybase DBMS.
Security Features: Complex, rules-based security configurable by Session Rules Book configuration file.
Constraints & Limitations:
|
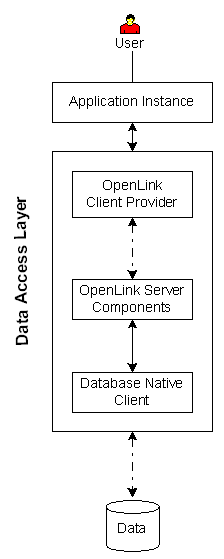 | Executive Summary: A client/server solution that provides enterprise grade data access with maximum configuration, security, and diagnostic resources.
No installation is required on data store server.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, OpenLink Server Components, Database Native Client, Data Repository.
Functional Capabilities: .NET data access to supported data stores.
Hardware/OS Dependencies: OpenLink Client Driver must be installed on a supported operating system that contains a functional JRE.
The JRE version may vary depending on the OpenLink client driver version..
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
OpenLink Server Components must be installed on a supported operating system.
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
Other Dependencies: OpenLink Server Components must reside on same machine as the Database Native Client.
Performance Levels: High performance.
Implementation Variances: OpenLink Server Components may reside on client operating system or a gateway.
Security Features:1) All Architectural Components may reside on one machine, 2) OpenLink server components and Database Native Client may reside on one, distinct gateway.
3) OpenLink server components and Database Native Client may reside on a distinct, DBMS server.
Constraints & Limitations: Overall performance and stability may be impacted by bottlenecks in the database native client.
|
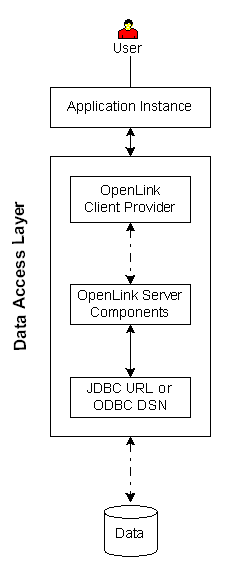 | Executive Summary: A client/server solution that provides enterprise grade data access with maximum configuration, security, and diagnostic resources.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, OpenLink Server Components, ODBC DSN or JDBC URL, Data Repository.
Functional Capabilities: Bridge-based .NET data access to data stores.
Hardware/OS Dependencies: OpenLink Client Driver must be installed on a supported operating system that contains a functional JRE.
The JRE version may vary depending on the OpenLink client driver version..
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
OpenLink Server Components must be installed on a supported operating system.
All architectural components on that operating system must share the same bit descriptor, i.e., 32 or 64 bit.
Other Dependencies: OpenLink Server Components must reside on same machine as a functional ODBC DSN or JDBC URL.
The ODBC DSN or JDBC URL may use OpenLink or non-OpenLink drivers.
Performance Levels: High performance.
Implementation Variances: 1) All architectural components may reside on one machine, 2) OpenLink Server Components and ODBC DSN or JDBC URL may reside on a gateway, 3) OpenLink Server Components and ODBC DSN or JDBC URL may reside on the data store server.
Security Features: Complex, rules-based security configurable by Session Rules Book configuration file.
Constraints & Limitations: Solution applies only to data stores that are accessible via ODBC DSNs or JDBC URLs.
Overall functionality, performance, and stability may be impacted by limitations in the ODBC DSN or JDBC URL.
|

Users are humans or non-human agents that leverage applications to obtain or manipulate SQL data held in data repositories.
Users are identified by the hostname or IP address of the machine which hosts their target application(s).

The application instance refers to individual instances of applications that users exploit in the target architecture.
Each instance of the application(s) is tasked with returning SQL data to users in a manner that is meaningful to them.

The
OpenLink Client Provider refers to
OpenLink's ADO .NET Provider.

The driver manager is a generic utility that loads drivers when requested to do so by client applications.
OpenLink's Windows-based drivers are compatible with the Microsoft Driver Manager.
OpenLink's Mac and Unix drivers ship with the iODBC Driver Manager.
However, these drivers are designed for interoperability with non-
OpenLink driver managers such as unixODBC and Intersolv.

The
OpenLink client driver comprises a clientside-only install of a .dll or other library and supporting files.
Single-Tier Client Drivers are DBMS- or Bridge-specific.
They establish ODBC connectivity without the assistance of server components.
Multi-Tier ODBC Client Drivers are generic.
They require
OpenLink Server Components to complete any data requests.

Database native client refers to third-party database client communications software that facilitates connectivity to the target data store.
This software speaks the native protocol of that data store.
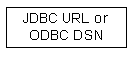
ODBC DSN or JDBC URL refers to ODBC Data Sources or JDBC Connection URLs that pre-exist on the client system.
These DSNs or JDBC URLS often use 3rd-party data access products, but they may use
OpenLink UDA as well.

The
OpenLink server components are architectural components that are specific to the Multi-Tier product format.
The server components consist of a Request Broker and an Agent.
The Request Broker is a generic, TCP-based listening service.
It responds to client driver requests and loads the Agent that is suited for fulling those client requests.
Agents may be DBMS- or bridge- specific.
Requets for Oracle data would be satisfied by one of
OpenLink's Oracle Database Agents.
Requests for data contained in a JDBC data store would be satisfied by one of
OpenLink's bridge-based JDBC agents.

Data refers to SQL data that is contained in the target data repository or repositories.

Local IPC communications between architectural components.
Local IPC communications can only occur when architectural components are hosted on the same, physical machine.
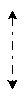
TCP/IP-based communications between architectural components.
TCP/IP-based communications can occur across machine boundaries.





 Users are humans or non-human agents that leverage applications to obtain or manipulate SQL data held in data repositories.
Users are identified by the hostname or IP address of the machine which hosts their target application(s).
Users are humans or non-human agents that leverage applications to obtain or manipulate SQL data held in data repositories.
Users are identified by the hostname or IP address of the machine which hosts their target application(s).
 The application instance refers to individual instances of applications that users exploit in the target architecture.
Each instance of the application(s) is tasked with returning SQL data to users in a manner that is meaningful to them.
The application instance refers to individual instances of applications that users exploit in the target architecture.
Each instance of the application(s) is tasked with returning SQL data to users in a manner that is meaningful to them.
 The
The  The driver manager is a generic utility that loads drivers when requested to do so by client applications.
The driver manager is a generic utility that loads drivers when requested to do so by client applications.
 The
The  Database native client refers to third-party database client communications software that facilitates connectivity to the target data store.
This software speaks the native protocol of that data store.
Database native client refers to third-party database client communications software that facilitates connectivity to the target data store.
This software speaks the native protocol of that data store.
 ODBC DSN or JDBC URL refers to ODBC Data Sources or JDBC Connection URLs that pre-exist on the client system.
These DSNs or JDBC URLS often use 3rd-party data access products, but they may use
ODBC DSN or JDBC URL refers to ODBC Data Sources or JDBC Connection URLs that pre-exist on the client system.
These DSNs or JDBC URLS often use 3rd-party data access products, but they may use  The
The  Data refers to SQL data that is contained in the target data repository or repositories.
Data refers to SQL data that is contained in the target data repository or repositories.
 Local IPC communications between architectural components.
Local IPC communications can only occur when architectural components are hosted on the same, physical machine.
Local IPC communications between architectural components.
Local IPC communications can only occur when architectural components are hosted on the same, physical machine.
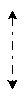 TCP/IP-based communications between architectural components.
TCP/IP-based communications can occur across machine boundaries.
TCP/IP-based communications between architectural components.
TCP/IP-based communications can occur across machine boundaries.