ODBC Data Access Drivers - Logical Diagrams
This section provides logical diagrams forSingle-Tier (Express Edition) Drivers
All Drivers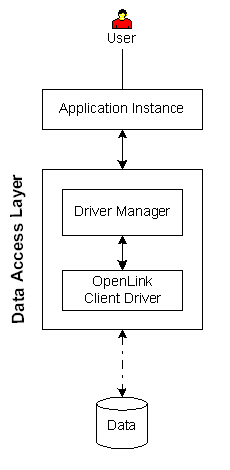
|
Executive Summary: A clientside-only solution that provides non-enterprise grade data access with minimal configuration and a low price point.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: ODBC data access to supported data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Data store version must be supported. Performance Levels: Non-enterprise grade performance. Implementation Variances: Data store may reside on the client machine or a remote machine. Security Features: Constraints & Limitations: Solution does not provide enterprise grade performance or stability. Solution is not portable to Unix clients. |
Single-Tier (Lite Edition) Drivers
Microsoft SQL Server,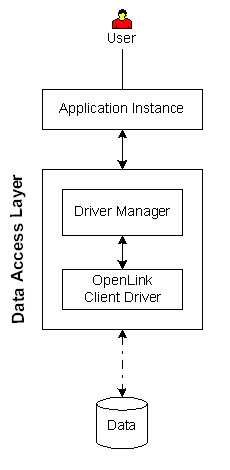
|
Executive Summary: A clientside-only solution that provides enterprise grade data access with minimal configuration.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: ODBC data access to supported data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Data store version must be supported. Performance Levels: Highest performance available. Implementation Variances: Data store may reside on the client machine or a remote machine. Security Features: Constraints & Limitations: Solution only applies to Microsoft SQL Server, |
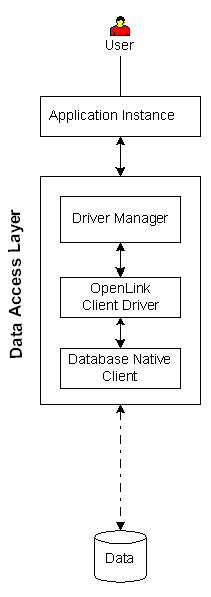
|
Executive Summary: A clientside-only solution that provides enterprise grade data access with minimal configuration.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: ODBC data access to supported data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Data store version must be supported. Performance Levels: Highest performance available. Implementation Variances: Data store may reside on the client machine or a remote machine. Security Features: Constraints & Limitations: Solution applies to DB2, Informix, Ingres, Oracle and Progress data access. |
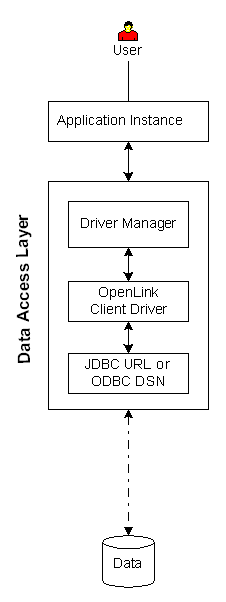
|
Executive Summary: A clientside-only solution that provides enterprise grade data access with minimal configuration.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: Bridge-based ODBC data access to ODBC- and JDBC- compliant data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Performance Levels: Highest performance available. Implementation Variances: Data store may reside on the client machine or a remote machine. Security Features: Constraints & Limitations: Solution applies only to data stores that are accessible via ODBC DSNs and JDBC URLs. Overall functionality, performance, and stability may be impacted by limitations in the ODBC DSN or JDBC URL. |
Multi-Tier Drivers
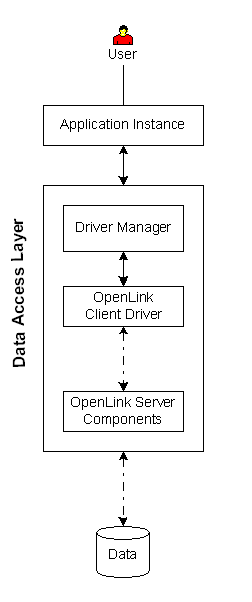
|
Executive Summary: A client/server solution that provides enterprise grade data access with maximum configuration, security, and diagnostic resources.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: ODBC data access to supported data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Performance Levels: High performance. Implementation Variances: 1) All architectural components may reside on one machine, 2) Security Features: Complex, rules-based security configurable by Session Rules Book feature. SSL available in Constraints & Limitations: |
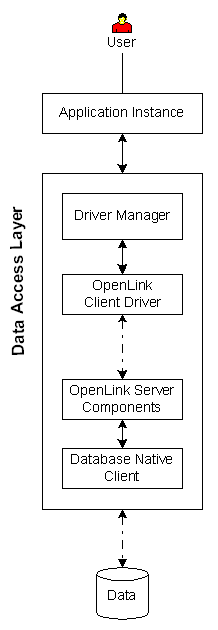
|
Executive Summary: A client/server solution that provides enterprise grade data access with maximum configuration, security, and diagnostic resources.
No installation is required on data store server.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: ODBC data access to supported data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Performance Levels: High performance. Implementation Variances:1) All architectural components may reside on one machine, 2) Security Features: Complex, rules-based security configurable by Session Rules Book feature. SSL available in Constraints & Limitations: Overall performance and stability may be impacted by bottlenecks in the database native client. |
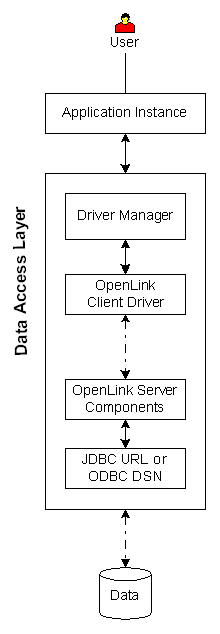
|
Executive Summary: A client/server solution that provides enterprise grade data access with maximum configuration, security, and diagnostic resources.
Architectural Components: Application Instance(s), Driver Manager, Functional Capabilities: Bridge-based ODBC data access to JDBC- and ODBC- compliant data stores. Hardware/OS Dependencies: Other Dependencies: Performance Levels: High performance. Implementation Variances: 1) All architectural components may reside on one machine, 2) Security Features: Complex, rules-based security configurable by Session Rules Book feature. SSL available in Constraints & Limitations: Solution applies only to data stores that are accessible via ODBC DSN or JDBC URLs. Overall functionality, performance, and stability may be impacted by limitations in the ODBC DSN or JDBC URL. |
 Users are humans or non-human agents that leverage applications to obtain or manipulate SQL data held in data repositories.
Users are identified by the hostname or IP address of the machine which hosts their target application(s).
Users are humans or non-human agents that leverage applications to obtain or manipulate SQL data held in data repositories.
Users are identified by the hostname or IP address of the machine which hosts their target application(s).
 The application instance refers to individual instances of applications that users exploit in the target architecture.
Each instance of the application(s) is tasked with returning SQL data to users in a manner that is meaningful to them.
The application instance refers to individual instances of applications that users exploit in the target architecture.
Each instance of the application(s) is tasked with returning SQL data to users in a manner that is meaningful to them.
 The driver manager is a generic utility that loads drivers when requested to do so by client applications.
The driver manager is a generic utility that loads drivers when requested to do so by client applications.
 The
The  Database native client refers to third-party database client communications software that facilitates connectivity to the target data store.
This software speaks the native protocol of that data store.
Database native client refers to third-party database client communications software that facilitates connectivity to the target data store.
This software speaks the native protocol of that data store.
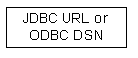 ODBC DSN or JDBC URL refers to ODBC data sources or JDBC connection URLs that pre-exist on the client system.
These DSNs or JDBC URLS often use 3rd-party data access products, but they may use
ODBC DSN or JDBC URL refers to ODBC data sources or JDBC connection URLs that pre-exist on the client system.
These DSNs or JDBC URLS often use 3rd-party data access products, but they may use  The
The  Data refers to SQL data that is contained in the target data store.
Data refers to SQL data that is contained in the target data store.
 Local IPC communications between architectural components.
Local IPC communications can only occur when architectural components are hosted on the same, physical machine.
Local IPC communications between architectural components.
Local IPC communications can only occur when architectural components are hosted on the same, physical machine.
 TCP/IP-based communications between architectural components.
TCP/IP-based communications can occur across machine boundaries.
TCP/IP-based communications between architectural components.
TCP/IP-based communications can occur across machine boundaries.
