Installation and Configuration of the Single-Tier "Express" Edition ODBC Driver for DB2 Data Sources, for Windows
Review Preinstallation Documentation: Pre-Installation Requirements
Installation
- The
OpenLink ODBC Driver for DB2 (Express Edition) is distributed as a Windows MSI installer. Double click on the installer 'ntl6edb2.msi' to commence the installation:

- This is the Welcome dialog for the
OpenLink ODBC Driver for Firebird (Express Edition):
- Read the Software License Agreement and accept before continuing your installation:
- Before installation, you will be prompted for a license file.
If a license file already exists on the machine, select the 'use existing file' option.
A trial (try) or full (buy) license can be obtained by selecting the 'try and buy' option, which loads our online try and buy web page:
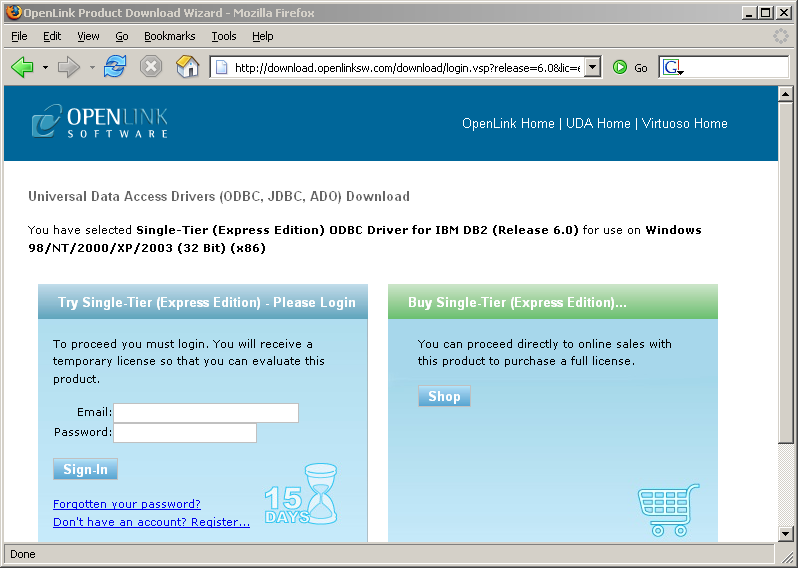
- To obtain the trial license, you must be a registered user on the
OpenLink Web site and login with the username (e-mail address) and password for that user. Click on the 'Shop' link to visit our online shop cart to purchase a full license, if required.
- Click on the 'download license' button to obtain an immediate license file and save it to your desktop.
Alternatively, mail can be sent to your e-mail address with a link to your
OpenLink Data Space (ODS). Here, all trial and full license files will be stored in a specialized Briefcase for download at a later date.
- Select the license file to be used for the installation:
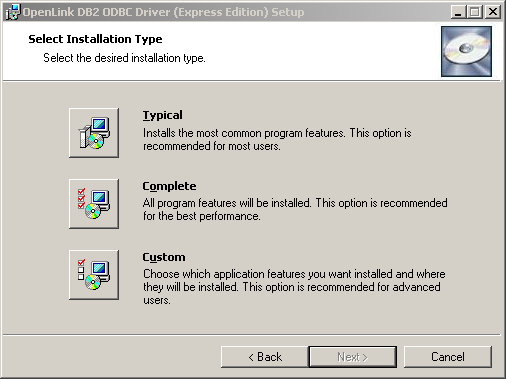
- Choose to perform a custom, typical, or complete installation of the driver:
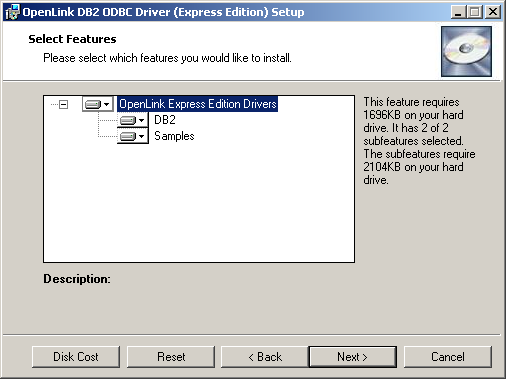
- Select the features to be installed:
- Click the install button to begin the installation:
- Installation in progress:
- The installation is complete and ready for use:
Configuration
- Launch the ODBC Administrator appropriate to the bitness (32-bit or 64-bit) of your client application and driver.
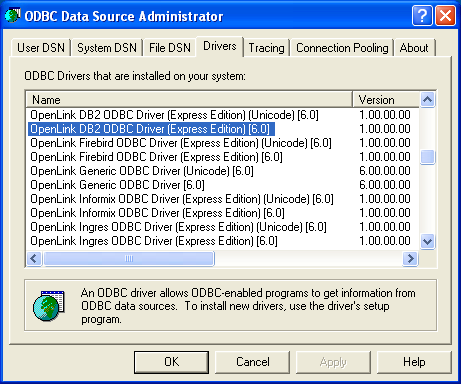
- Click on the Drivers tab to confirm that the driver has been successfully installed:
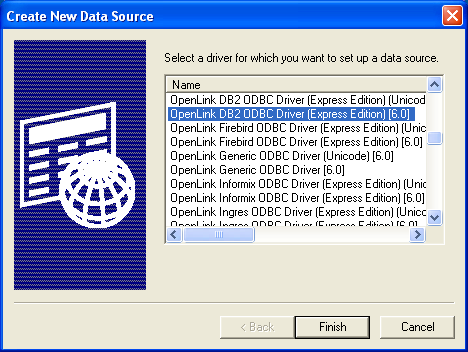
- From either the User or System DSN tab, click on the Add button and select the Express Edition Driver from the list.
Select the Unicode version of the driver if and only if you are working with multi-byte character sets, as unnecessary translations can significantly affect ODBC performance:
- On the Data Source tab, provide a suitable DSN name and optional description for the Data Source to be created:
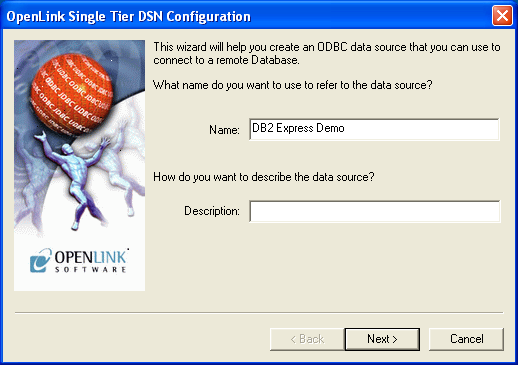
- The Connection tab requests the minimum parameters required to make a connection to the target database:
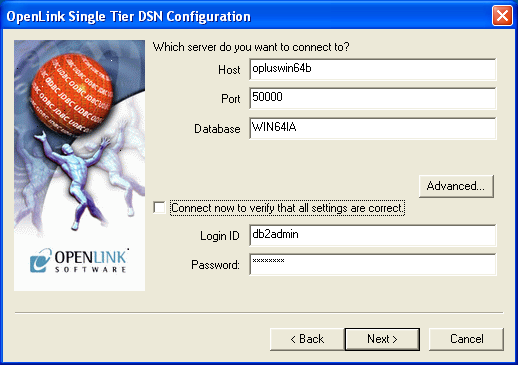
- Host: This is the fully qualified hostname, or IP address, of the machine hosting the DBMS you wish to access, e.g., dbms-server.example.com or 192.168.155.123.
Any hostname which can be resolved by your local DNS is acceptable.
- Port: This is the port on which DB2 is listening.
- Database: This is the name of a valid DB2 database alias to which you want to connect.
- Connect now to verify that all settings are correct: Will attempt to connect to the database, once you click Next.
- Login ID: This is a valid user for the DB2 database.
- Password: This is a valid password for the DB2 database.
- Host: This is the fully qualified hostname, or IP address, of the machine hosting the DBMS you wish to access, e.g., dbms-server.example.com or 192.168.155.123.
Any hostname which can be resolved by your local DNS is acceptable.
- The advanced button displays additional, optional parameters that can be configured:
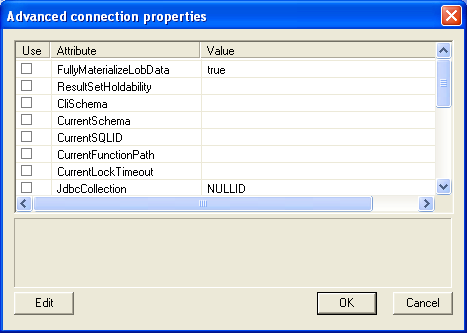
Name Description FullyMaterializeLobData Indicates whether the driver retrieves LOB locators for FETCH operations. The data type of this propery is boolean. If the value is true, LOB data is fully materialized within the JDBC driver when a row is fetched. If this value is false, LOB data is streamed. ResultSetHoldability Specifies whether cursors remain open after a commit operation. Valid values are 1- HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT or 2 - CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT. CLiSchema Specifies the schema of the DB2 shadow catalog tables or views that are searched when an application invokes a DatabaseMetaData method. CurrentSchema Specifies the default schema name that is used to qualify unqualified database objects in dynamically prepared SQL statements. This value of this property sets the value in the CURRENT SCHEMA special register on a server other than a DB2 UDB for z/OS server. Do not set this property for a DB2 UDB for z/OS server. CurrentSQLID Specifies the authorization ID that is used for authorization checking on dynamically prepared CREATE, GRANT, and REVOKE SQL statements. The owner of a table space, database, storage group, or synonym that is created by a dynamically issued CREATE statement. The implicit qualifier of all table, view, alias, and index names specified in dynamic SQL statements. CurrentFunctionPath Species the SQL path that is used to resolve unqualified data type names and function names in SQL statements that are in JDBC programs. The data type of this property is String. For a DB2 UDB for Linux, UNIX, and Windows server, the maximum length is 254 bytes. The value is a comma-separated list of schema names. Those names can be ordinary or delimited identifiers. CurrentLockTimeout Directs DB2 UDB for Linux, UNIX, and Windows servers to wait indefinitely for a lock or to wait for the specified number of seconds for a lock when the lock cannot be obtained immediately. The data type of this property is INT. A value of zero means no wait. A value of -1 means to wait indefinitely. A postive integer indicates the number of seconds to wait for a lock. JdbcCollection Specifies the collection ID for the packages that are used by an instance of the DB2 Universal JDBC Driver at run time. The data type of jdbcCollection is String. The default is NULLID. CurrentPackageSet Specifies the collection ID to search for DB2 packages for the DB2 Universal JDBC Driver. The data type of this property is String. The default is NULLID. If currentPackageSet is set, its value overrides the value of jdbcCollection. CurrentPackagePath Specifies a comma-separated list of collections on the server. The DB2 server searches these collections for the DB2 packages for the DB2 Universal JDBC Driver. The precedence rules for the currentPackagePath and currentPackageSet properties follow the precedence rules for the DB2 CURRENT PACKAGESET and CURRENT PACKAGE PATH special registers. SecurityMechanism Specifies the DRDA security mechanism. Possible values are: 3 - User ID and password, 4 - User ID only, 7 - User ID, encrypted password, 9 - Encrypted user ID and password, 11 - Kerberos. If this property is specified, the specified security mechanism is the only mechanism that is used. If the security mechanism is not supported by the connection, an exception is thrown. KerberosServerPrincipal For a data source that uses Kerberos security, this specifies the name that is used for the data source when it is registered with the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC). DeferPrepares Specifies whether to defer prepare operations until run time. The data type of this property is boolean. ClientUser Specifies the current client user name for the connection. This information is for client accounting purposes. Unlike the connection user name, this value can change during a connection. For a DB2 UDB for Linux, UNIX, and Windows servers, the maximum length is 255 bytes. ClientWorkstation Specifies the workstation name for the current client for the connection. This information is for client accounting purposes. This value can change during a connection. The data type of this property is String. For a DB2 UDB for Linux, UNIX, and Windows servers, the maximum length is 255 bytes. ClientApplicationInformation Specifies the application information for the current client for the connection. This information is for client accounting purposes. This value can change during a connection. The data type of this property is String. For a DB2 UDB for Linux, UNIX, and Windows servers, the maximum length is 255 bytes. ClientAccountingInformation Specifies accounting information for the current client for the connection. This information is for client accounting purposes. This value can change during a connection. The data type of this property is String. For a DB2 UDB for Linux, UNIX, and Windows servers, the maximum length is 255 bytes.
- Click continue to proceed to the Options dialog.
This dialog contains optional parameters that are not required for basic ODBC connectivity:
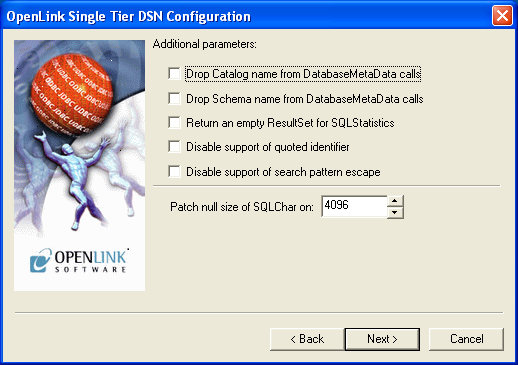
- Drop Catalog name from
DatabaseMetaData calls — Enable this option to have the catalog name not appear for tables, views, and procedures when requesting database meta-data.
- Drop Schema name from
DatabaseMetaData calls — Enable this option to have the schema-name not appear for tables, views, and procedures when requesting database meta-data.
- Return an empty
ResultSet for SQLStatistics — Check this box to have SQLStatistics() return an empty resultset. Use this if the underlying database does not support retrieval of statistics about a table (e.g. what indexes it has).
- Disable support of quoted identifier — If set, the call
SQLGetInfo for 'SQL_IDENTIFIER_QUOTE_CHAR' will return a space (" "). It can be used if the DBMS doesn't support quoted SQL like select * from "account."
- No support of search string escape — If set, the call
SQLGetInfo for 'SQL_LIKE_ESCAPE_CLAUSE' will return a space (" "). It can be used if the DBMS doesn't support SQL escape patterns.
- Patch of null size of SQL_CHAR on — If set, this option overrides the size of SQL_CHAR column type returned by the database with the value set in the text box (in bytes).
With a default value of 0, the driver uses the size returned by the database.
- Drop Catalog name from
- Click continue to proceed to the Preferences dialog.
This dialog contains optional parameters that are not required for basic ODBC connectivity:
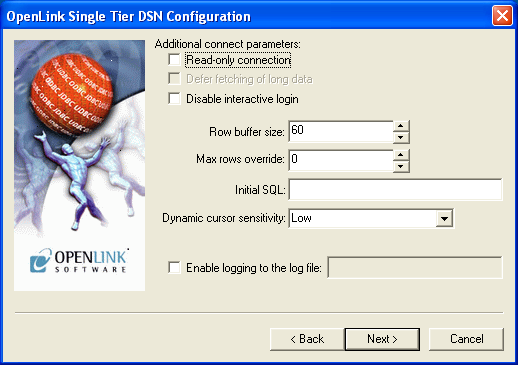
- Read Only connection — Specifies whether the connection is "Read-only." Make sure the checkbox is unchecked to request a "Read/Write" connection.
- Defer fetching of long data — Defers fetching of LONG (BINARY, BLOB etc.) data unless explicitly requested in a query.
This provides significant performance increases when fields in query do not include LONG data fields.
- Disable interactive login — Suppresses the ODBC "Username" and "Password" login dialog boxes when interacting with your ODBC DSN from within an ODBC compliant application.
- Row Buffer Size — This attribute specifies the number of records to be transported over the network in a single network hop.
Values can range from 1 to 99.
- Max Rows Override — Allows you to define a limit on the maximum number of rows to be returned from a query.
The default value of 0 means no limit.
- Initial SQL — Lets you specify a file containing SQL statements that will be run automatically against the database upon connection.
- Dynamic cursor sensitivity — Enables or disables the row version cache used with dynamic cursors.
When dynamic cursor sensitivity is set high, the Cursor Library calculates checksums for each row in the current rowset and compares these with the checksums (if any) already stored in the row version cache for the same rows when fetched previously.
If the checksums differ for a row, the row has been updated since it was last fetched and the row status flag is set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED.
The row version cache is then updated with the latest checksums for the rowset.
From the user's point of view, the only visible difference between the two sensitivity settings is that a row status flag can never be set to SQL_ROW_UPDATED when the cursor sensitivity is low.
(The row status is instead displayed as SQL_ROW_SUCCESS.) In all other respects, performance aside, the two settings are the same.
Deleted rows don't appear in the rowset.
Updates to the row since the row was last fetched are reflected in the row data, and inserted rows appear in the rowset, if their keys fall within the span of the rowset.
If your application does not need to detect the row status SQL_ROW_UPDATED, you should leave the 'High Cursor Sensitivity' checkbox unchecked, as performance is improved.
The calculation and comparison of checksums for each row fetched carries an overhead.
If this option is enabled, the table oplrvc must have been created beforehand using the appropriate script for the target database.
- Enable logging to the log file — Pass a full path to an arbitrary log file that will be used to log ODBC API and SQL related errors.
- Read Only connection — Specifies whether the connection is "Read-only." Make sure the checkbox is unchecked to request a "Read/Write" connection.
- Click Next to continue to the Compatibility dialog . The Compatibility dialog enables you to set additional parameters to enhance compatibility with applications:
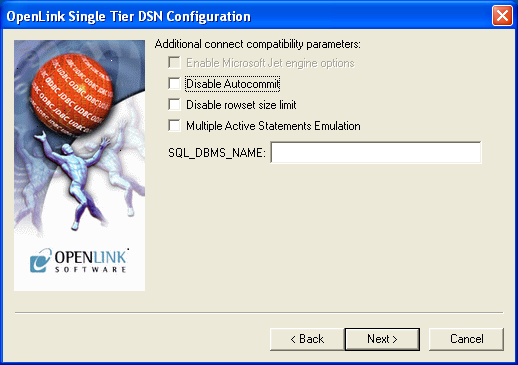
- Disable Autocommit — Change the default commit behaviour of the
OpenLink Lite Driver. The default mode is AutoCommit mode (box unchecked).
- Disable Rowset Size Limit — Disable the limitation enforced by the cursor library.
The limitation is enforced by default to prevent the Driver claiming all available memory in the event that a resultset is generated from an erroneous query is very large.
The limit is normally never reached.
- Multiple Active Statements Emulation — Enables use of Multiple Active statements in an ODBC application even if the underlying database does not allow this, as it is emulated in the driver.
- SQL_DBMS Name — Manually overrides the
SQLGetInfo(SQL_DBMS_NAME) response returned by the driver. This is required for products like Microsoft InfoPath for which the return the value should be "SQL Server."
- Disable Autocommit — Change the default commit behaviour of the
- Click on the Test Data Source button to verify that a successful connection can be made to the database.
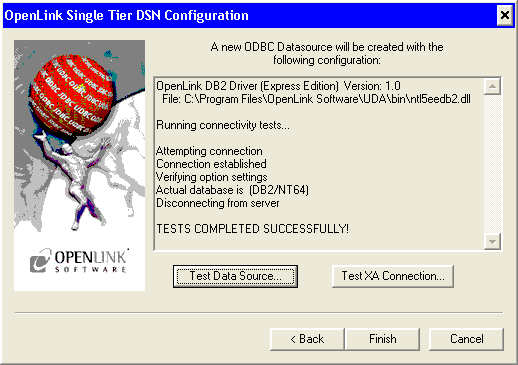
Next...
- Test your DSNs with our sample program.
- If anything isn't working as you expect, including errors resulting from the test above, see our Troubleshooting Resources.
- Should you decide to purchase a commercial license at the end of your evaluation period, be sure to consult our documentation which explains the placement and uptake of commercial license files and the use of our
OpenLink License Manager technology: License Technology & Application.
